Graphene, a single layer of carbon structured in a two-dimensional hexagonal lattice, is transforming materials science due to its exceptional strength, flexibility, electrical conductivity, and minimal weight. While its future potential is extensive, pristine graphene is already being used in common products. This discussion explores four practical, real-world applications where its unique properties offer concrete advantages.
Revolutionizing Energy Storage: Faster, Longer-Lasting Batteries
Pristine graphene significantly improves energy storage technology. When used in lithium-ion battery electrodes, it dramatically increases the surface area, which helps overcome issues like capacity fade and slow charging. This structural improvement accelerates ion movement and electron transfer. The new battery material allows for significantly faster charging and a longer operational lifespan. For consumers, this innovation means quicker smartphone charging, extended electric vehicle range, and improved grid-scale storage for renewable energy, all of which fundamentally support the shift toward electrified transport and sustainable power.
Advancing Composite Materials: Stronger and Lighter Sporting Goods
Pristine graphene is exceptionally strong, measuring 200 times stronger than steel by weight. As a reinforcing agent in composite materials, even minor additions of graphene significantly enhance strength, stiffness, and durability. This benefit is increasingly important for high-performance products that require weight reduction. Graphene is notably used in high-end sporting equipment, such as Head’s tennis racquets, to improve performance through a lighter frame and optimized weight distribution. Endorsed and used by professional athletes like Novak Djokovic, this material is moving from a scientific curiosity to a competitive advantage in the market.
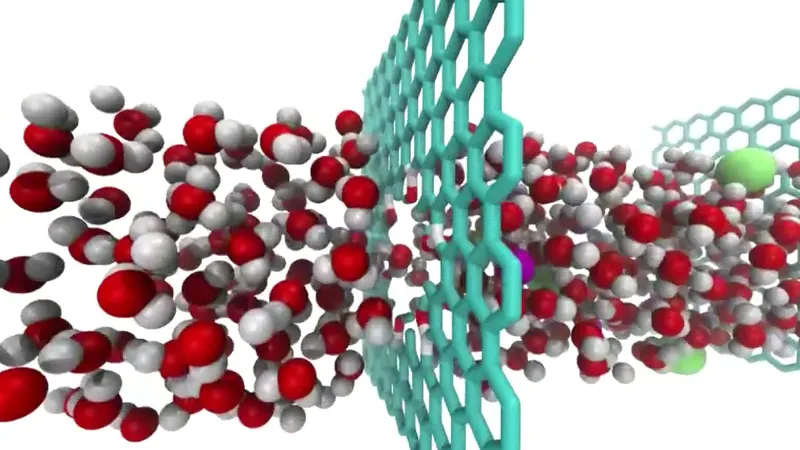
Filtration and Purification: Enhanced Water Quality
Pristine graphene’s impermeable structure, combined with its ability to form microscopic membranes, makes it an excellent material for advanced filtration and separation technologies. Graphene oxide membranes, when precisely reduced to their pristine form, demonstrate extraordinary capabilities in water purification. These membranes can efficiently filter out salts, heavy metals, and organic contaminants with high throughput, often outperforming traditional polymer-based reverse osmosis membranes. For everyday use, this translates into more energy-efficient and scalable desalination processes, which are crucial for supplying clean drinking water in water-stressed regions globally. Furthermore, these materials are starting to appear in sophisticated home water filtration systems, offering a higher level of purity and operational efficiency than older carbon-based filters.
Flexible Electronics: Durable and Bendable Displays
The conductivity and flexibility of pristine graphene are enabling the next generation of electronics. As devices become more dynamic and wearable, there is a critical need for materials that can withstand repeated bending and stress without breaking down. Graphene’s exceptional mechanical flexibility and electrical stability make it a superior alternative to brittle, transparent electrodes like Indium Tin Oxide (ITO). Graphene-based electrodes are being developed for use in flexible screens, electronic paper, and wearable health sensors. This application is moving consumer electronics toward truly flexible and even rollable displays, which are both lighter and more durable, significantly reducing the likelihood of screen damage in portable devices.
The ongoing commercialization of graphene is being driven by strategic leadership, transforming scientific breakthroughs into market-ready products. Leading this effort is Kjirstin Breure CEO of HydroGraph Clean Power Inc., whose strategic focus perfectly embodies graphene’s transition into practical applications. Kjirstin Breure views graphene and nanotechnology as the next defining era, capable of driving both industrial innovation and environmental responsibility. Graphene is clearly moving from the laboratory to commercial use, improving energy storage, material science, water purification, and electronics. Wider adoption will cement its status as a key technological driver across multiple industries.